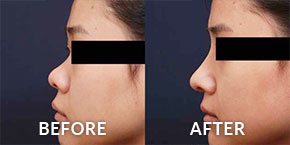
Fat Grafting
 Fat Grafting is a procedure involving the harvesting, purification, and injection of fat from one area of the body into another part of the body. Often times, the injection site is on the face. The entire procedure is usually quick, simple, and involves very little discomfort or scarring.
Fat Grafting is a procedure involving the harvesting, purification, and injection of fat from one area of the body into another part of the body. Often times, the injection site is on the face. The entire procedure is usually quick, simple, and involves very little discomfort or scarring.
Why Fat Grafting?
Fat Grafting targets people who are bothered by the noticeable signs of aging.
As people age, loss of volume around the midface (i.e., areas between the cheeks, nose, and lower eyelid) and/or general fat loss in the face can lead to an older and unhealthy appearance. Thus, by restoring lost fat to a person’s face, this procedure can be used to achieve a healthier, more vibrant look.
Additionally, Fat Grafting can also be used to enhance the facial profile through a more beautifully contoured shape. Thus, for many people, Fat Grafting provides an alternative to facial bone surgery. Considering facial bone surgery can be expensive, painful, and often involves a lengthy recovery time.
For many patients interested in changing the contour of their face, fat grafting can be an advantageous alternative.
Advantages of Fat Grafting
For older patients with depressed wrinkles or facial volume loss, the use of collagen based fillers (Artecoll), cadaver skin (Alloderm), or hyaluronic acid-based gel fillers (Restylane, Juvederm) offer a temporary solution and are not ideal for large surface areas in facial contouring.
Thus, one of the main advantages of Fat Grafting is that it can be used for overall facial contouring in older patients.
Other advantages of Fat Grafting are no allergic reactions, minimal pain and discomfort, and nominal side effects associated with the procedure. In addition, the procedure is considered fairly safe, and since it requires no incision, there are no long-term visible scars in the results. Furthermore, compared to fillers (e.g., Restylane, Juvederm, etc.), Fat Grafting is a cheaper, more economical alternative. In general, Fat Grafting also has a fairly quick recovery time, so depending on the extent of the procedure, a person may return to normal daily activities in as little as one day.
Disadvantages of Fat Grafting
- Up to 50% fat resorption
- Prolonged swelling and bruising
- Irregular results
- Fat hardening – especially when Fat Grafting is used to contour the breast or buttocks, since a large amount of fat is injected into ne area at one time
- Minor discomfort during the fat harvesting and/or fat re-injecting process
- In rare cases, Fat Grafting has also been known to lead to infections
Procedure
Generally, a small blunt needle is used to remove fat from either the abdomen or the thighs.
The harvested fat is then processed, and the removed fat is optimized to prevent reabsorption (i.e., when the fat is absorbed and there is a loss of substance) through the use of a special filtering process of awake liposuction , where any oil and serum is separated from the fat.
When the harvested fat is processed, multiple filtering systems are applied to purify the fat and to prevent damage to the fat cells. Furthermore, the loss of growth factors in the fat is minimized during the fat purification process. Thus, the filtering process both improves the fat graft survival rate and maximizes fat maintenance at the injection site (i.e., the area where the fat graft is re-injected into the body) resulting in better, longer lasting results.
Generally, the entire procedure is fairly simply and associated with very little to no scarring or discomfort.
Post-Operative Care
- Aspirin
- Plavix
- Coumadin
- Celebrex
- Fish oil/omega-3
- Herbal medication, red ginseng concentrates
- Any blood thinning medications
In case of prescribed medications, please inform the office. The prescribing doctor’s approval is required before discontinuing the medication. Please remove any metallic jewelry (earrings, necklaces, etc) before the surgery. They may interfere with surgical equipment. Please wear a comfortable, loose buttoned-down or zipped shirt along with loose pants or long skirts on the day of your surgery. You want to be as comfortable as possible during the surgery.
You must arrange a legal guardian or caregiver who will provide you transportation after the surgery.
You will not be allowed to drive after the surgery. Please take your prescribed medications as usual (excluding blood thinning medications) on the day of your surgery. If you take blood pressure medications on a daily basis, bring extra on the day of your surgery to present to the nurse.
Duration of Surgery
Less than an hour
Anesthesia Options
The entire procedure is done under local anesthesia.
Post-Operative Care
Like other procedures, swelling is expected after fat grafting. The swelling will become most severe 2-3 days after the surgery, but critical swelling will subside within one week. However, patients may resume their daily activities the day after the surgery.
After the surgery, it is extremely important that patients DO NOT rub the area until the transferred fat becomes attached to its new place. About three weeks after surgery, the structure becomes stable and all normal activities can be resumed.
Recovery Time
Depending on the location and extent of the procedure, recovery time can last anywhere from 1 day to 3 weeks.
Expected Results
- A more beautifully contoured shape.
- A more youthful, vibrant look.
Although Fat Grafting was not designed to correct wrinkles, by subtly increasing the volume of an aging face, this procedure can also minimize the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Additional Information
Ongoing research in the use of stem cells in Fat Grafting means that this procedure now produces longer lasting results.
Some conditions that could be improved with this procedure include the following: General facial fat and/or soft tissue loss with aging, depressed forehead, sunken upper eyelid, lower eyelid wrinkle, loss in lower eyelid youthfulness, depressed (i.e., recessed or sunken areas of the body and/or face) forehead and/or temple, asymmetric forehead and/or temple, depressed areas below the lower eyelid and/or inner cheek region (i.e., midface), deep nasolabial fold (i.e., creases along the sides of a person’s nose that continue to the corners of the mouth), aging hands, wrinkles, fine lines, depressed scars, aging face with loss in volume, wide cheekbones, flat face, and/or retruded (i.e., recessed or caved in) face.
- Facial Regions
- Upper eyelid, lower eyelid, youthful eyelid
- Lips, forehead, temple, cheek, cheekbone, nasolabial fold, chin, nose
- Breast
- Hip
- Hands